TechBuzz
Additive Manufacturing in Jewellery: How 3D Printing is Shaping the Future
Discover how additive manufacturing (3D printing) is revolutionizing the jewellery industry with rapid prototyping, precision design, and sustainable production techniques.

What is Additive Manufacturing?
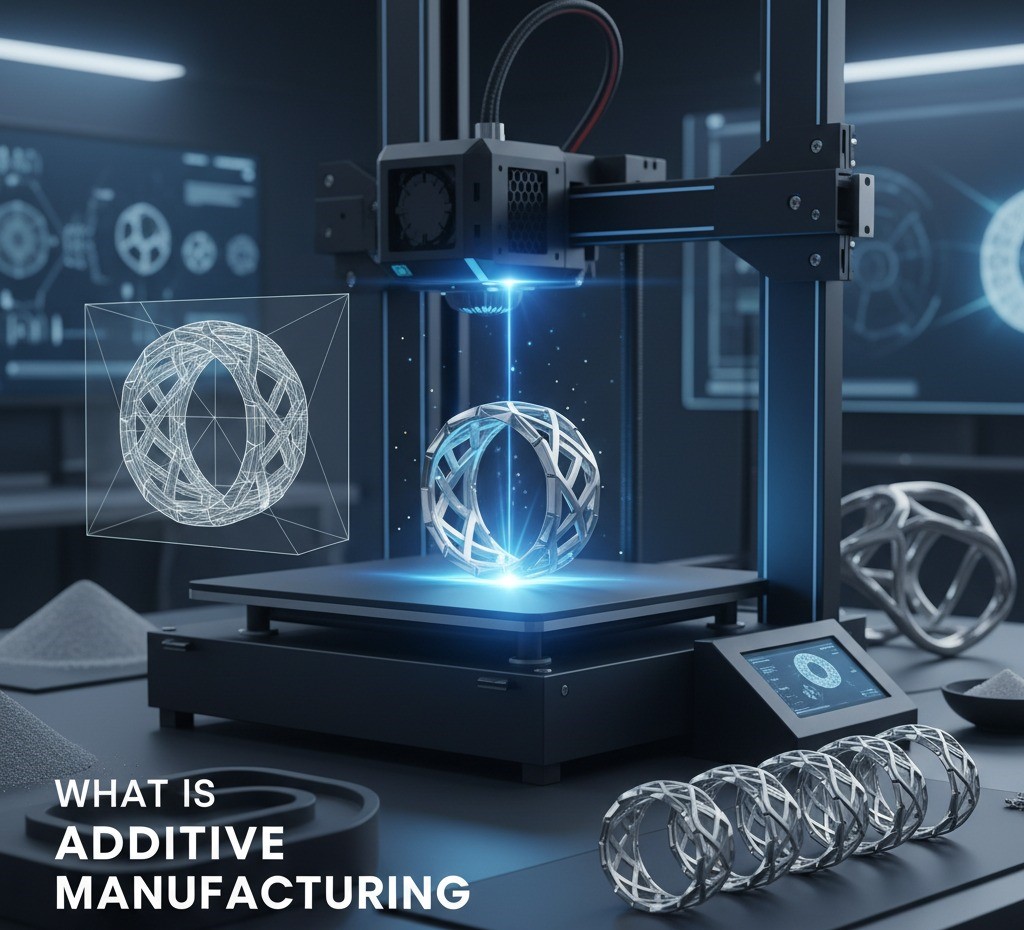
Additive manufacturing (AM), commonly known as 3D printing, is the process of building objects layer by layer directly from a 3D CAD model. Unlike traditional methods, AM doesnŌĆÖt require cutting tools or molds, enabling designers and manufacturers to create intricate, customized, and functional parts efficiently.
Applications in Jewellery and Beyond
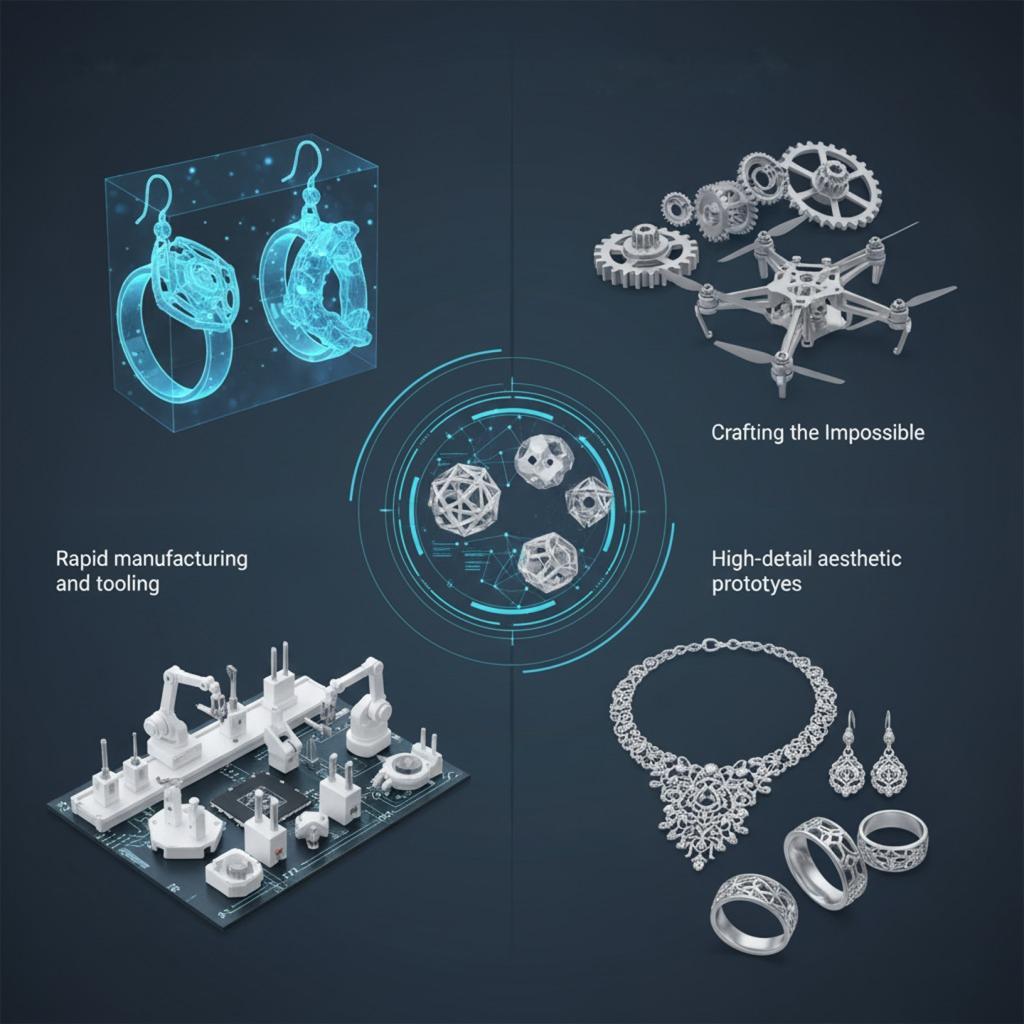
Additive manufacturing is widely used for:
- Rapid prototyping and concept models
- Production of functional parts and spare components
- Rapid manufacturing and tooling
- High-detail aesthetic prototypes
In jewellery, AM allows designers to craft complex motifs and precise structures that are otherwise impossible with traditional methods.
Popular Additive Manufacturing Processes

- Stereolithography (SLA) ŌĆō Uses UV light to cure photopolymer resin, producing highly detailed, smooth-finish prototypes.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) ŌĆō Sintered thermoplastic powders create durable, functional parts with complex geometries.
- Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) ŌĆō Offers fast, accurate, and cost-effective production of functional parts using inkjet fusing agents.
- PolyJet Printing ŌĆō Enables multi-material, multi-color parts with fine detail, ready for immediate use.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) ŌĆō Fuses metal powders like stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium for strong, precise, and lightweight components.
Materials Used in Additive Manufacturing

- Resins: High-finesse prototypes with smooth surfaces
- Nylon Powder: Flexible, heat-resistant, ideal for SLS
- Metal Powder: Strong and durable parts for DMLS applications
Why Additive Manufacturing is Transforming Jewellery
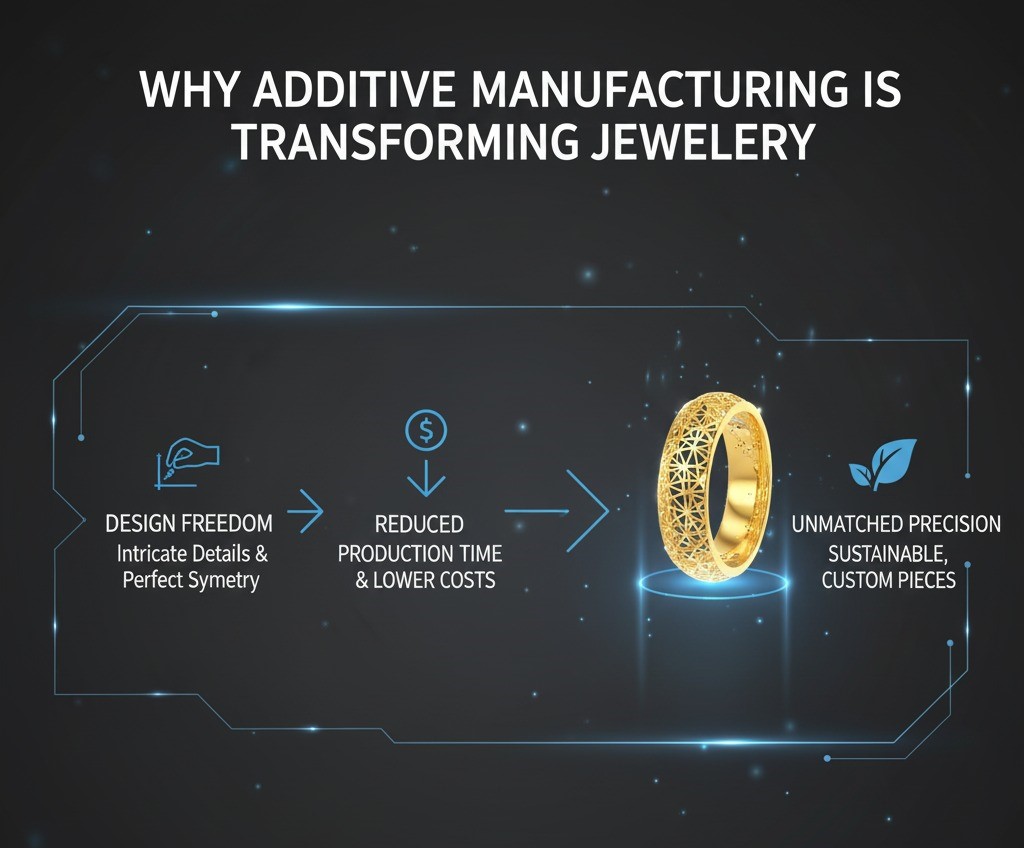
AM reduces production time, lowers costs, and enhances design freedom, allowing jewellery brands to innovate faster. Designers can experiment with intricate details, achieve perfect symmetry, and create custom, sustainable pieces with unmatched precision.
The Future of Jewellery and Manufacturing

Additive manufacturing is not just a toolŌĆöitŌĆÖs a creative revolution. By combining digital design, precision engineering, and material innovation, AM is enabling the next generation of jewellery designers and manufacturers to dream bigger and create smarter.
JB Insights
Jewellery machinery is vital investment for global competitiveness

JBExlusive
Jewel Buzz recently hosted a high-level panel featuring the titans of the jewelry manufacturing industry to discuss the significance of the JMAIIE 2026. The Panel of Stalwarts comprised :K Srinivasan: Chairman, Emerald Group,Dr. Chetan Kumar: CMD, Lakshmi Diamonds, Bengaluru Nitesh Jain, MD, Purple Jewels Private Limited,Nikhil Ranavat: Director, AR Gold Private Limited & Director, Swarnshilp Chains and Jewels Pvt Ltd
The discussion highlighted how technology is no longer an optional expense but a vital investment for global competitiveness. The importance of machinery was summed by said K Srinivasan: Investing in machinery is not an expenditure; it is an investment.
Key Objectives for JMAIIE 2026
The leaders identified several critical reasons for attending the expo, emphasizing that the “machinery-only” focus of JMAIIE allows for deep concentration without the distractions of finished jewelry.
- Technology Upgradation:┬Ā K Srinivasan emphasized that with 41 years in the field, he views quality machinery as the foundation for working with all gold purities (from 9k to 22k) and silver. Continuous updating is required to stay relevant.
- Cost & Loss Reduction:┬Ā Nikhil Ranawat pointed out that with rising gold prices, the priority is minimizing manufacturing losses. Even recovering an extra 1% of gold through better technology significantly impacts the bottom line.
- Weight & Aesthetics: Dr. Chetan Kumar noted the industry’s shift toward both ultra-lightweight and complex fashionable jewelry, both of which require advanced precision tools.
- Production Efficiency:┬Ā Nitesh Jain highlighted the need for robust, “non-breakdown” machines to keep manufacturing costs low for the end consumer.
The State of “Make in India” Machinery
The panel offered a candid assessment of domestic vs. international machinery standards:
| Strengths of Indian Machinery | Areas for Improvement |
| Outstanding quality in Enameling, Casting Furnaces, and Buffing Machines. | Chain-making technology still lags behind global standards. |
| Excellence in CAD/CAM software and implementation. | Need for more robust, long-term durability to match Italian/Western builds. |
| High value-for-money and improving after-sales service. | Consistency in high-end finishing for luxury products. |
Future Outlook
The industry leaders called for a strategic shift to align with the Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India) vision.
- Technology Hubs: Dr. Chetan Kumar said government support was imperative and proposed the creation of a dedicated Technology Park for the jewelry industry where manufacturers and AI researchers can collaborate on new machinery.
- Skill Development:┬Ā Nitesh Jain warned that high-tech machines are useless without a skilled workforce trained to operate them. A cultural shift from traditional handmade methods to tech-driven manufacturing is essential.
- Global Ambitions: With the conclusion of various FTAs (Free Trade Agreements), the panel believes that superior technology will allow India to truly become the “Jeweler to the World.”
Conclusion
JMAIIE 2026 stands as a pivotal platform for the industry. The consensus is clear: the future of Indian jewelry lies in the marriage of traditional hand-craftsmanship and cutting-edge technology.
-

 DiamondBuzz6 hours ago
DiamondBuzz6 hours agoBotswana Diamonds rebrands as Botswana Minerals PLC
-

 DiamondBuzz6 hours ago
DiamondBuzz6 hours agoDespite revenue growth in jewellery sector, natural diamond upstream sees stagnation
-

 International News8 hours ago
International News8 hours agoIndia Pavilion at HK twin shows showcases exceptional craftsmanship
-

 International News8 hours ago
International News8 hours agoGold continues to get strength on the Middle East conflict





